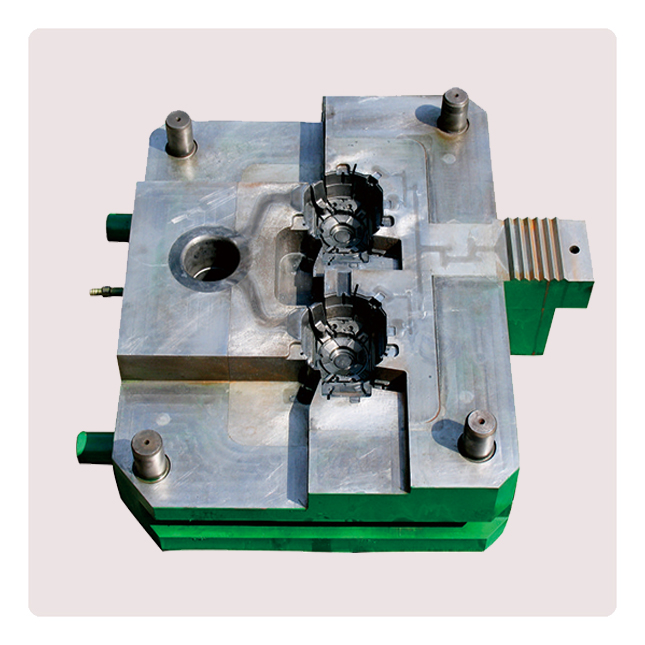
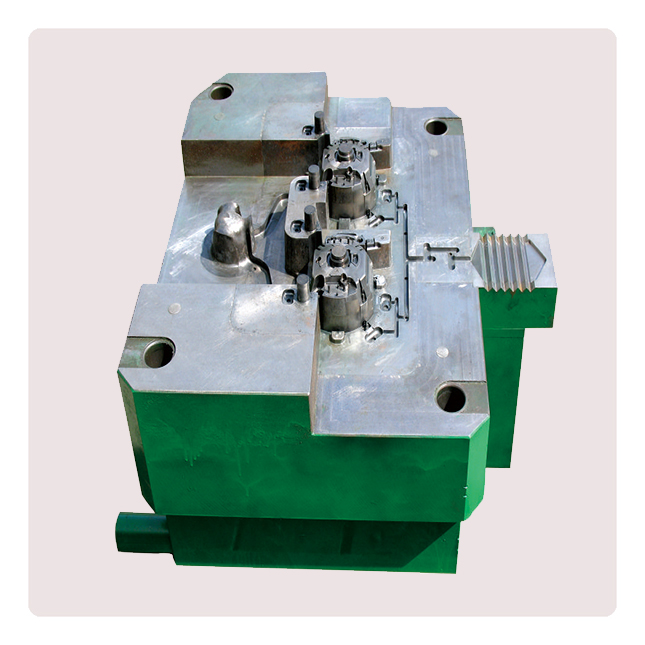
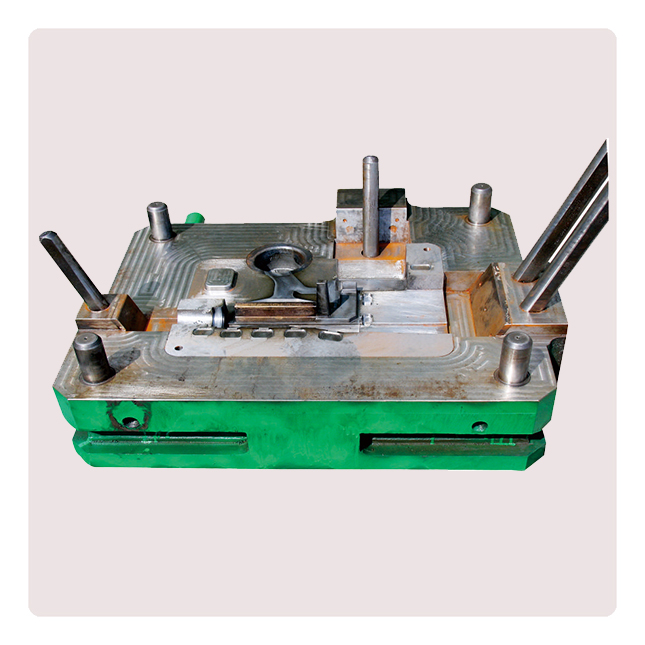
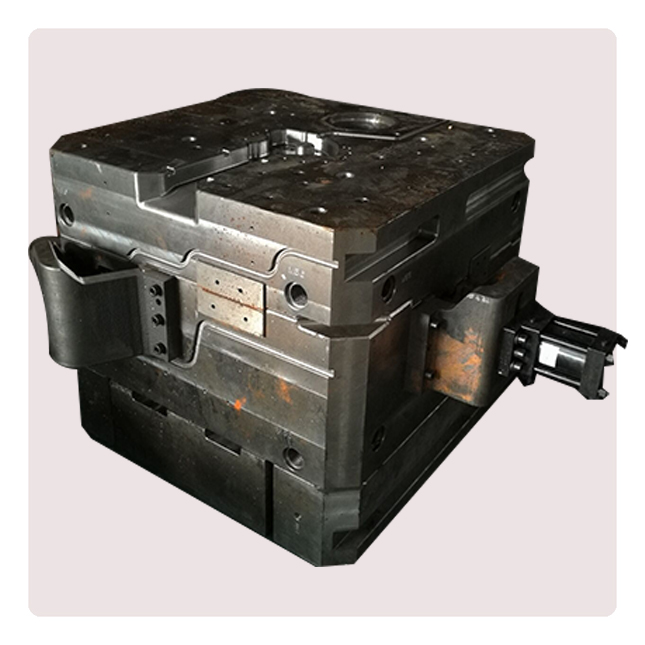
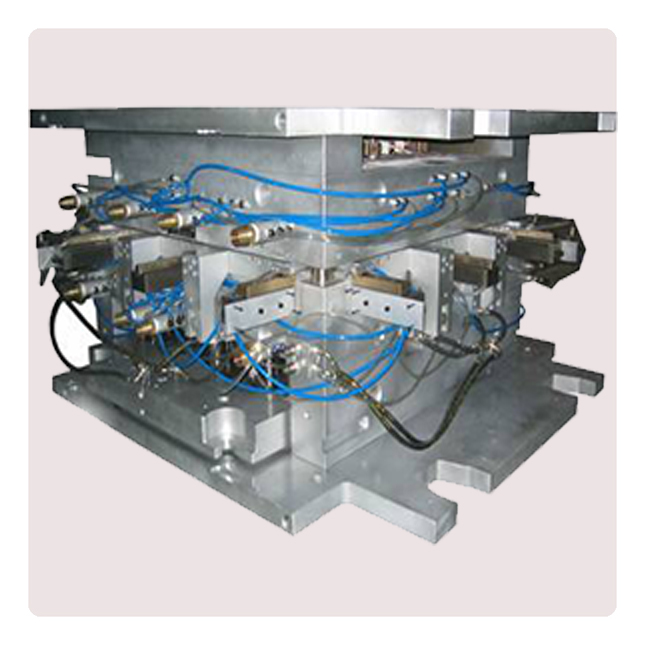
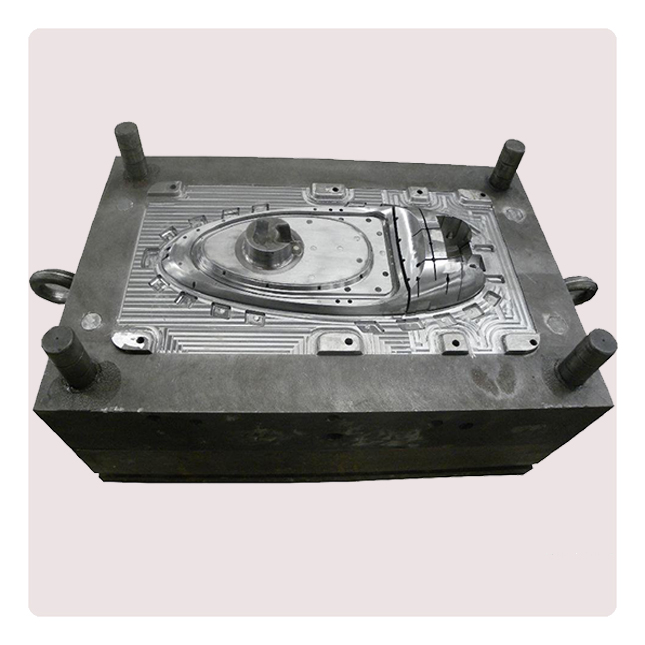
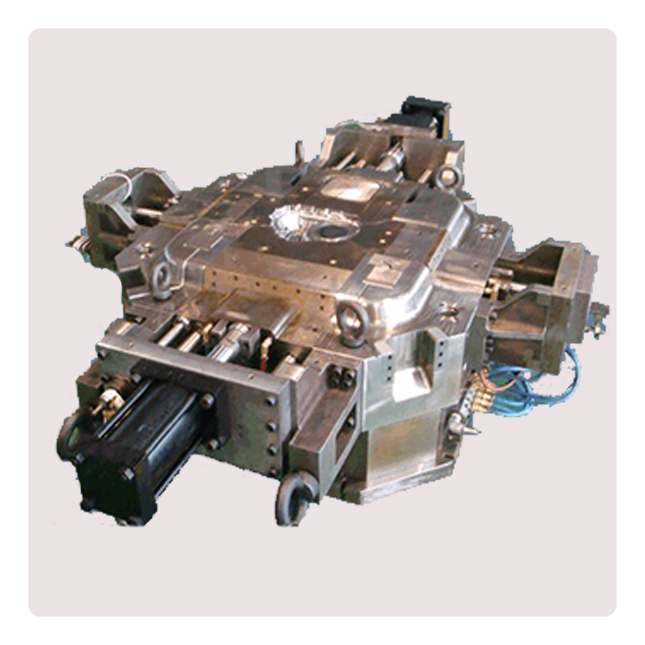
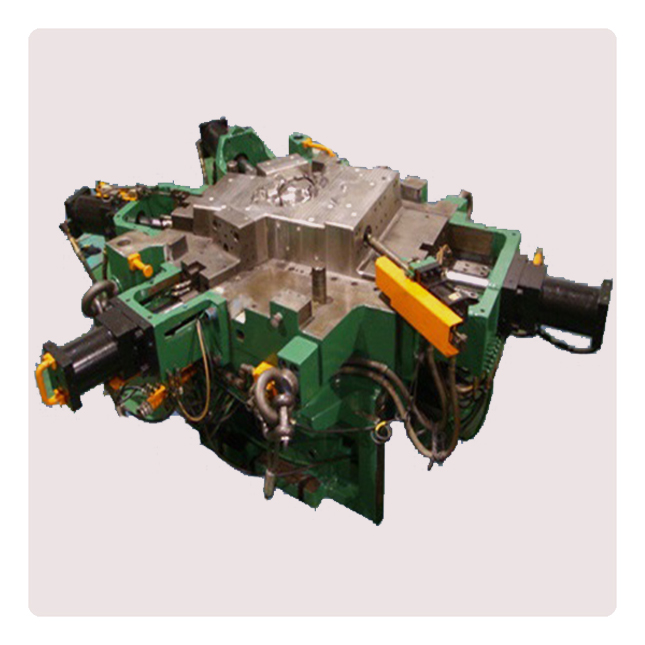
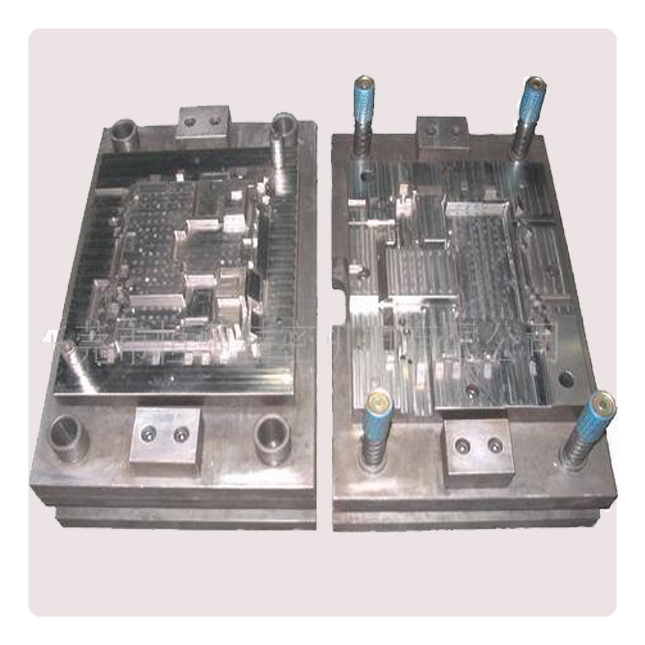
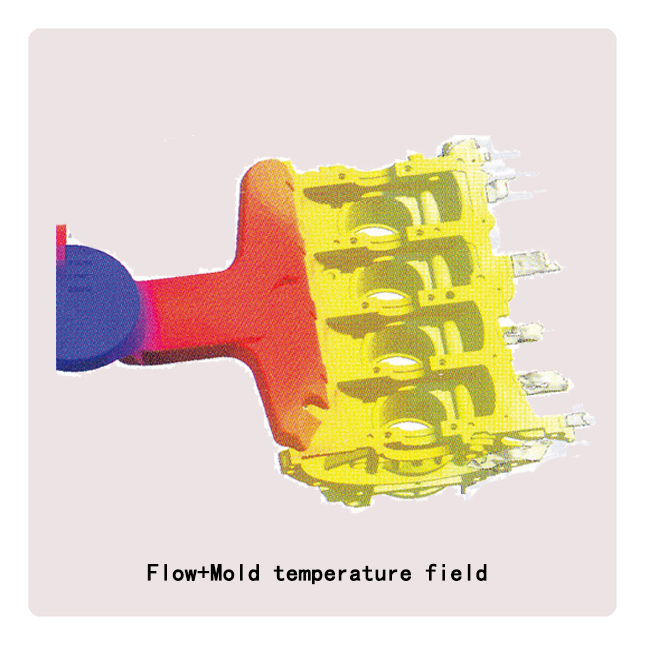
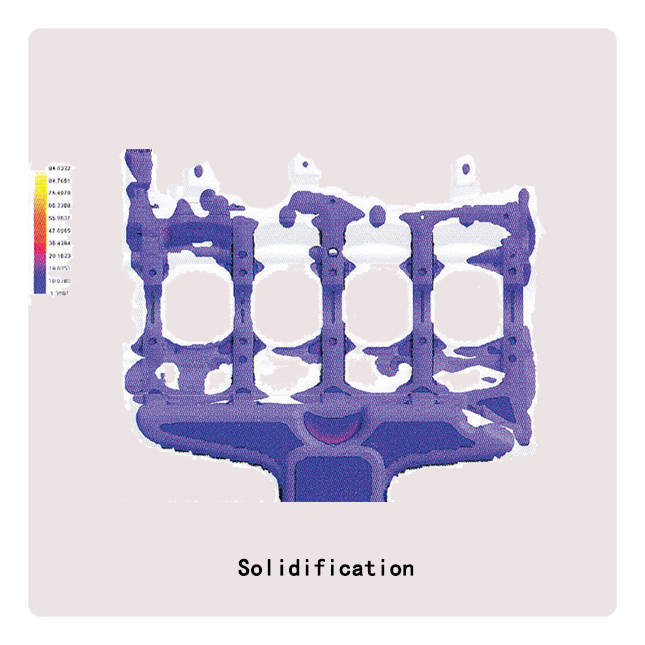
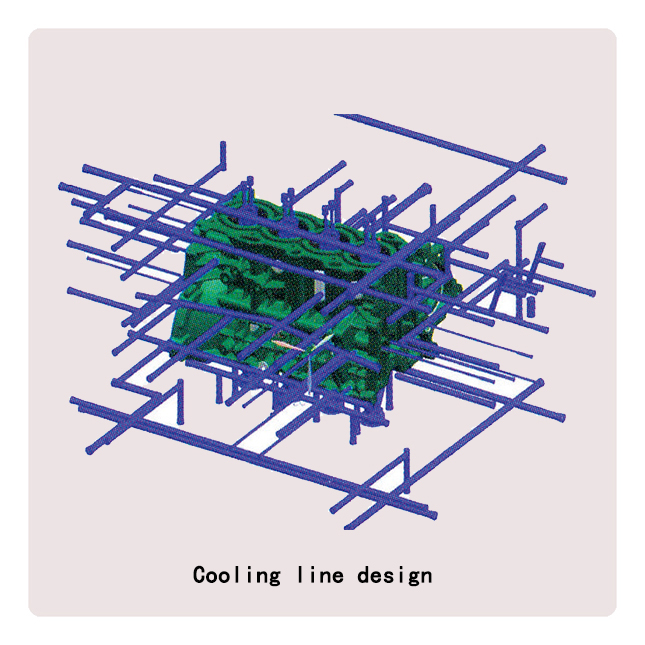
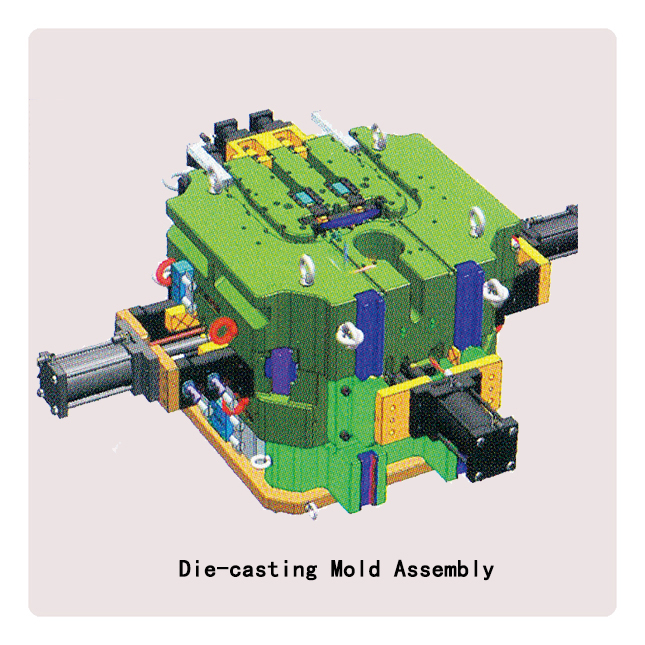
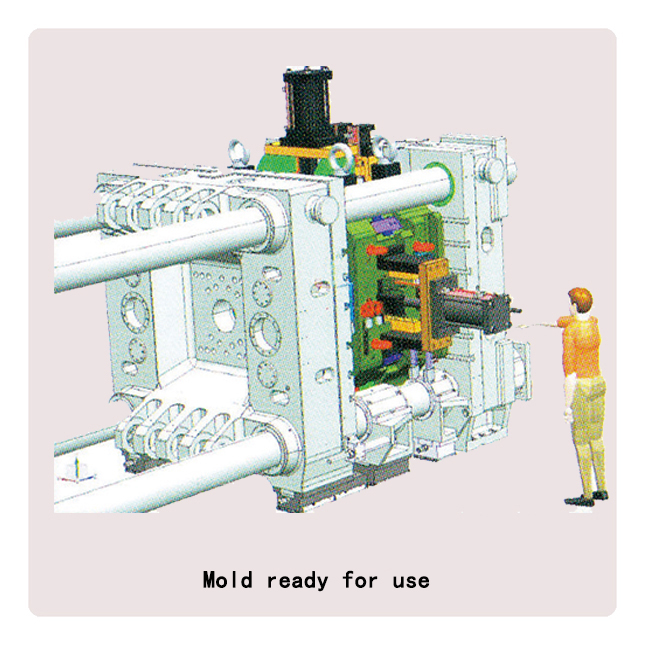
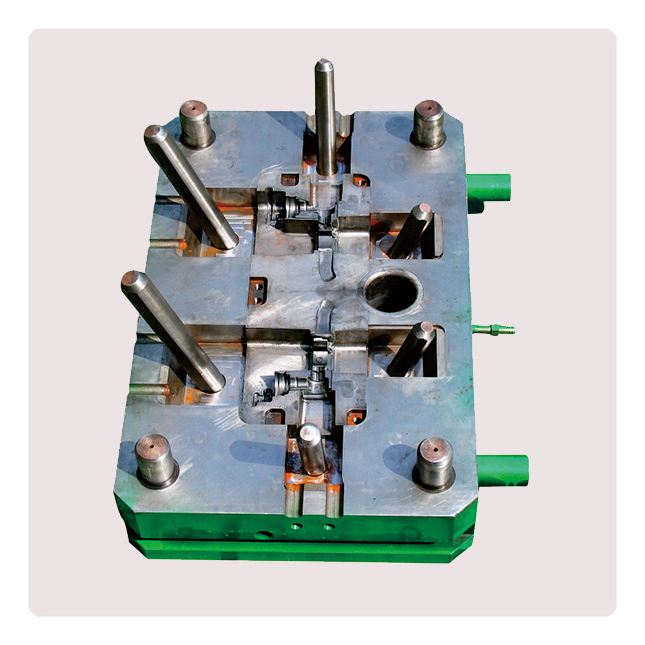
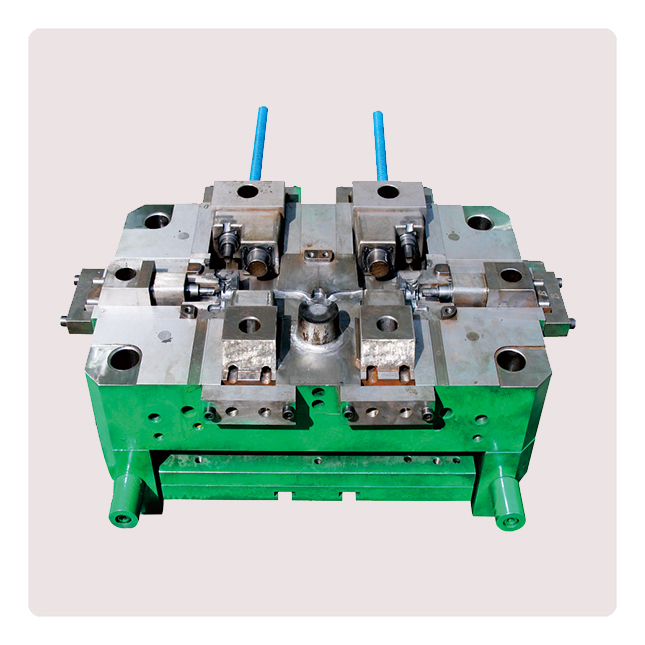
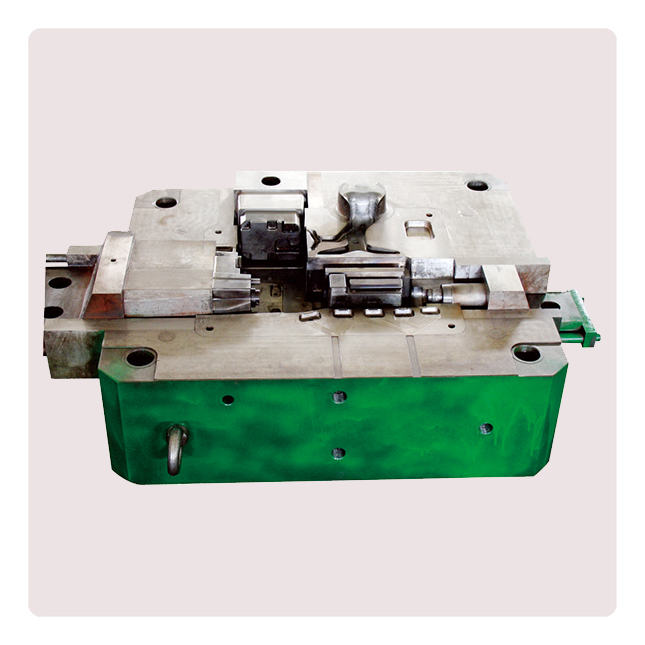
Die-casting mold
The Importance of Mold Design
Mold design is one of the most important steps in the process because the shape and attributes of the mold will directly affect the final product. The die casting procedure forces molten metal into molds using high pressure and it requires a mold with exact specifications to achieve the task.
Mold design affects the shape, configuration, quality, and uniformity of a product created through the die casting procedure. Improper specifications can result in tool or material corrosion, as well as inferior product quality, while an effective design can improve efficiency and production time.
Factors Contributing to Quality Mold Design
There are a number of mold design factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate specifications for a project. Some of these factors include:
Draft
Draft is the degree to which a mold core can be tapered. A precise draft is needed to smoothly eject the casting from the die, but since draft is not constant and varies according to the angle of the wall, features such as the type of molten alloy used, shape of the wall, and depth of the mold can affect the process. Mold geometry can also influence draft. In general, untapped holes require tapering, due to the risk of shrinkage. Likewise, inner walls can also shrink, and therefore require more drafting than outer walls.
Fillets
A fillet is a concave junction used to smooth an angled surface. Sharp corners can hinder the casting process, so many molds have fillets to create rounded edges and reduce the risk of production errors. With the exception of the parting line, fillets can be added nearly anywhere on a mold.
Parting Line
The parting line, or parting surface, connects different sections of the mold together. If the parting line is imprecisely positioned or becomes deformed from work strain, material may seep through the gap between the mold pieces, leading to non-uniform molding and excessive seaming.
Bosses
Bosses are die cast knobs that serve as mounting points or stand-offs in mold design. Manufacturers often add a hole to the interior structure of the boss to ensure uniform wall thickness in a molded product. Metal tends to have difficulty filling deep bosses, so filleting and ribbing may be necessary to alleviate this problem.
Ribs
Die cast ribs can be used to improve material strength in products lacking the wall thickness required for certain applications. Selective rib placement can reduce the chance of stress cracking and non-uniform thickness. It is also beneficial for decreasing product weight and improving fill capabilities.
Holes and Windows
Including holes or windows in a die cast mold directly affects the ease of ejecting a completed molding and enables the creation of substantial drafts. Additional features, such as overflows, flashovers, and cross feeders may be necessary to prevent unwanted casting within the holes or poor material flow around the holes.
Symbols
Manufacturers often include brand names or product logos in the mold design of die-cast products. While symbols do not typically complicate the die casting process, their use can affect production costs. In particular, a raised logo or symbol requires additional molten metal volume for each manufactured part. Conversely, a recessed symbol requires less raw material and can reduce expenses.
Die and component material and hardness for various cast metals
The most important material properties for the dies are thermal shock resistance and softening at elevated temperature; other important properties include hardenability, machinability, heat checking resistance, weldability, availability (especially for larger dies), and cost. The longevity of a die is directly dependent on the temperature of the molten metal and the cycle time.13] The dies used in die casting are usually made out of hardened tool steels, because cast iron cannot withstand the high pressures involved, therefore the dies are very expensive, resulting in high start-up costs.[14] Metals that are cast at higher temperatures require dies made from higher alloy steels.
| Die and component material and hardness for various cast metals | ||||||
| Die component | Cast metal | |||||
| Tin, lead & zinc | Aluminum & magnesium | Copper & brass | ||||
| Material | Hardness | Material | Hardness | Material | Hardness | |
| Cavity inserts | P20 | 290–330 HB | H13 | 42–48 HRC | DIN 1.2367 | 38–44 HRC |
| H11 | 46–50 HRC | H11 | 42–48 HRC | H20, H21, H22 | 44–48 HRC | |
| H13 | 46–50 HRC | |||||
| Cores | H13 | 46–52 HRC | H13 | 44–48 HRC | DIN 1.2367 | 40–46 HRC |
| DIN 1.2367 | 42–48 HRC | |||||
| Core pins | H13 | 48–52 HRC | DIN 1.2367 prehard | 37–40 HRC | DIN 1.2367 prehard | 37–40 HRC |
| Sprue parts | H13 | 48–52 HRC | H13 DIN 1.2367 | 46–48 HRC 44–46 HRC | DIN 1.2367 | 42–46 HRC |
| Nozzle | 420 | 40–44 HRC | H13 | 42–48 HRC | DIN 1.2367 H13 | 40–44 HRC 42–48 HRC |
| Ejector pins | H13 | 46–50 HRC | H13 | 46–50 HRC | H13 | 46–50 HRC |
| Plunger shot sleeve | H13 | 46–50 HRC | H13 DIN 1.2367 | 42–48 HRC 42–48 HRC | DIN 1.2367 H13 | 42–46 HRC 42–46 HRC |
| Holder block | 4140 prehard | ~300 HB | 4140 prehard | ~300 HB | 4140 prehard | ~300 HB |
● The main failure mode for die casting dies is wear or erosion. Other failure modes are heat checking and thermal fatigue. Heat checking is when surface cracks occur on the die due to a large temperature change on every cycle. Thermal fatigue is when surface cracks occur on the die due to a large number of cycles.
| Typical die temperatures and life for various cast materials | ||||
| Zinc | Aluminum | Magnesium | Brass (leaded yellow) | |
| Maximum die life [number of cycles] | 1000000 | 100000 | 100000 | 10000 |
| Die temperature [C° (F°)] | 218 (425) | 288 (550) | 260 (500) | 500 (950) |
| Casting temperature [C° (F°)] | 400 (760) | 660 (1220) | 760 (1400) | 1090 (2000) |
● Why Choose Us?
● 20+ Years of consistent, reputable service in the die-casting mold industry.
● Use Pro-E, UG, Ci-matron to provide the best Mold design, and die-casting mold flow analyzing adopts Japanese ADSTTWFAN casting simulation analysis software. Also we can make samples by 3D printer before die-casting Mold manufacture if customer demand.
● Full machining capabilities of die-casting mold material, including the most up to date Large-scale CNC, Wire flame cutter, High-speed CNC, WEDM-LS equipment, Rocker drill
● In house Inspection Department, with CMM, Spectrum analyzer, Million-pixels X-Ray, Tensile tester, Length measurer, Crystalline phase analyzer, Projection measurer, Ageing tester, Salt water spray test device, Hardness tester.
● Highly qualified, CAD/CAM educated engineering staff.
Contact us today for more details!